Lebanon: MED GAIMS is opening the eyes of Directorate General of Antiquities to more gamification applicability

Menjez is a village located in the Akkar District overlooking the “El-Kabir" river which forms the northern boundary between Lebanon and Syria. Its Name is of Syriac origin meaning "saver" or "concealer". The village is famous for its vernacular houses built with the basalt stone, typical of the region. It encloses an important number of archaeological and historical monuments including the Roman Temple of Makam El Rab in addition to hundreds of megalithic tombs dating back to the bronze age. The village is inscribed in the tentative list of UNESCO world heritage sites.
The temple of Makam El-Rab (meaning the sanctuary of the Lord) or also named Beit Jaaluk is located on a hill overlooking the village of Menjez, on the road once crossed by the caravans from the Phoenician coast towards the hinterland, especially Homs, Baalbek and Palestine. The temple, built with basalt stone, dates back to the first century A.D. and is dedicated to Nemesis, the goddess of wealth and fate. Several inscribed dedications were found in the temple, one of which is engraved on a base of a statue dedicated to Nemesis, represented by a wheel under the name of the priest by whom it was offered. In the Byzantine period, the temple was turned into a church.
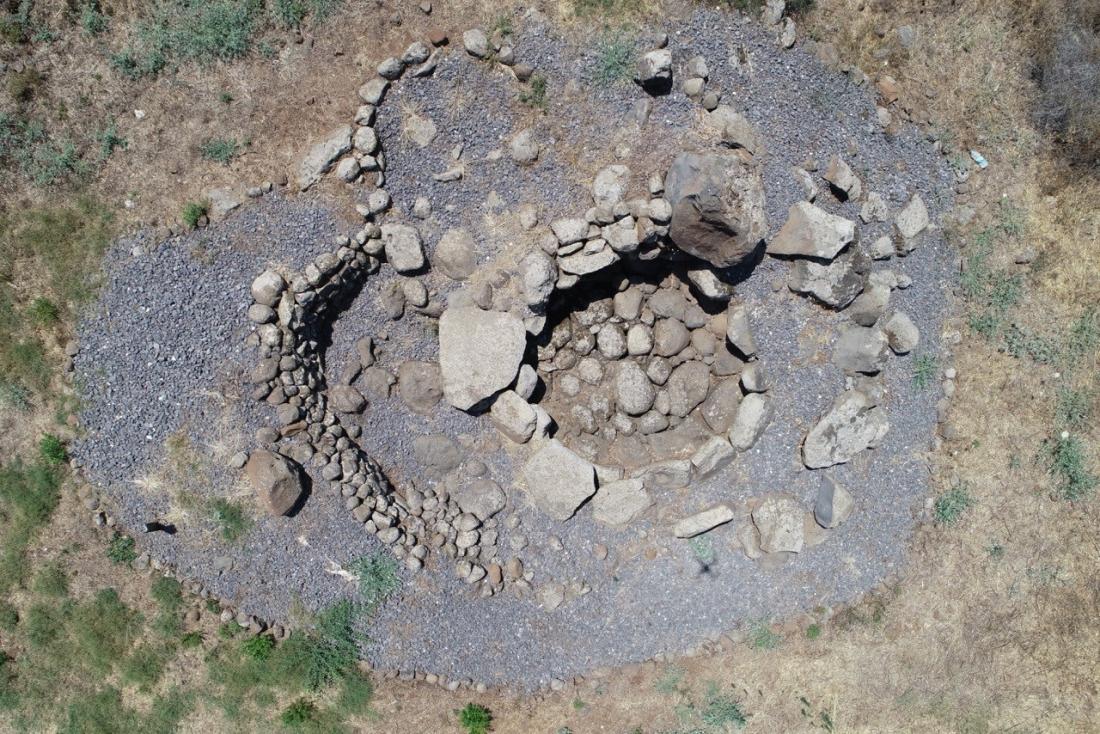
The Megalithic Tombs, dating back to the Early Bronze Age and built with basalt stone, are located within the village of Menjez and its vicinity. More than a hundred of tombs with different shapes have been discovered. The burial rooms are oval, circular or rectangular. The burial rituals remain uncovered due to the absence of a complete skeleton. In the sixties of the last century, 87 burials were studied by the Jesuit father Maurice Talon. On 2018-2019, 11 tombs were rehabilitated in the framework of a research and valorization project of megalithic tombs. While on 2021, the Megalithic Tombs were digitized, drawn and 3D modelled.