MEDISS contrasts the effects of water salinization to increase date palm productivity in Jericho - Palestine

From 7 to 12 of February, the consultancy firm TIMESIS, contracted by Palestinian Wastewater Engineers Group (PWEG), MEDISS lead partner, made the second round of in-depth study of soil in an extensive area planted with date palm in collaboration with the Governorate of Jericho and with the coordination of the PWEG project leader.
The research was aimed at the analysis and characterization of soils.
14 sites were chosen, in which soil samples were taken and delivered to Al Quds University of Jerusalem, Department of Environmental Sciences. The samples will be analyzed to evaluate the real fertility of Jericho soil, especially with reference to the salinity content.
During the mission, several meetings were held with date palm growers who described the cultivation technique in use. The cultivated variety is the Medjoul, much appreciated abroad for its large size. The smaller fruits are instead marketed nationally and to produce "ajua", that is date paste used in different types of confectionery.
TIMESIS also met with the president of the "Palm Farmer Cooperative Association in Jericho and Jordan Valley - PFCA" who is also president of the Jericho Water Users Association.
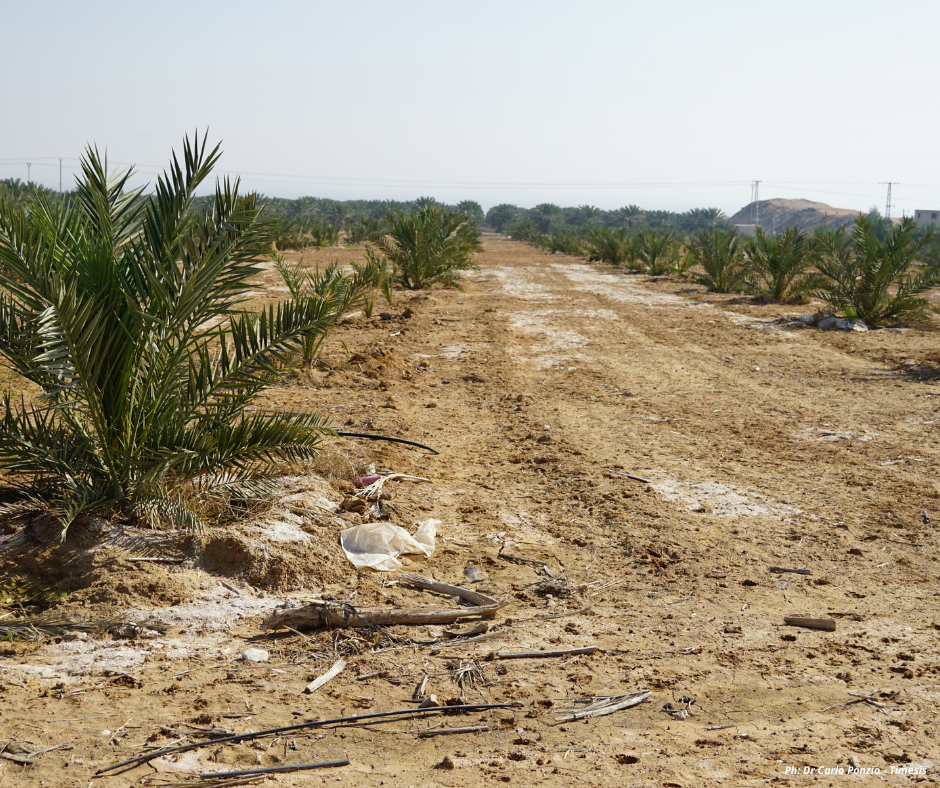
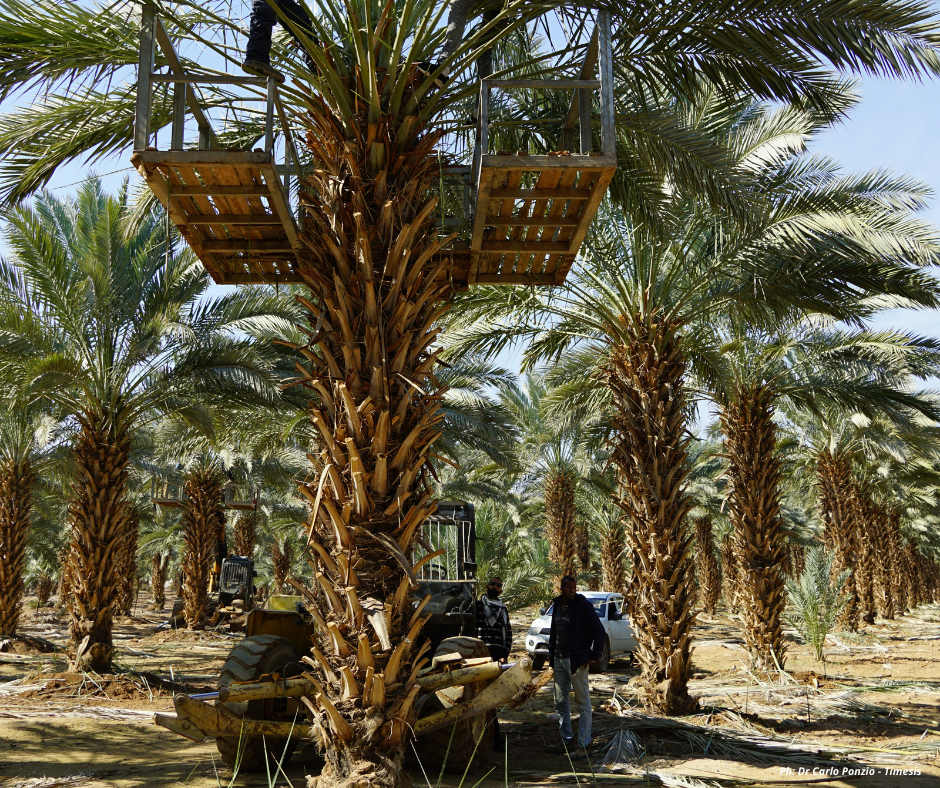


The two organizations are strongly integrated and beneficiaries of the MEDISS project. In fact, a collective irrigation network is under construction, which will reach a length of about 30 kilometers, to serve all associated companies. To date, the water pipeline built is 16 km.
Irrigation water is currently supplied only by 4 wells, whose water has problems of excessive salinity. Analyzes are underway to assess the exact impact of salinization on agriculture.
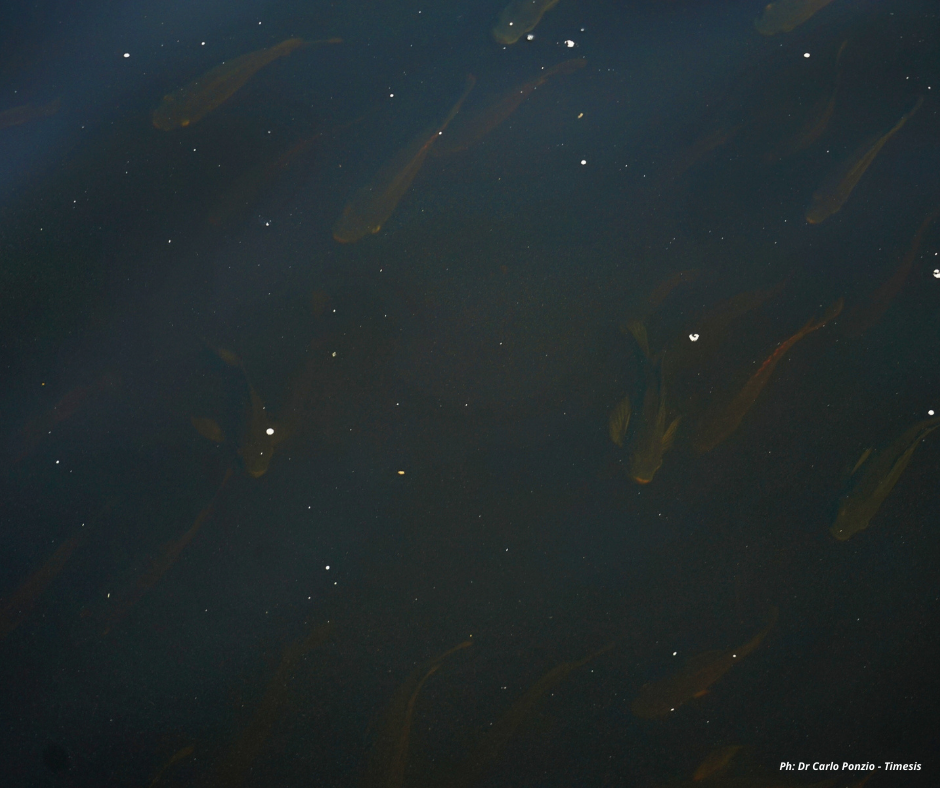
The MEDISS project aims to increase the water available to the network and improve its quality by blending it with purified water from Jericho Wastewater Treatment Plant. The fish in the tank of the treatment plant testifies to the quality of the effluent achieved with the treatment.
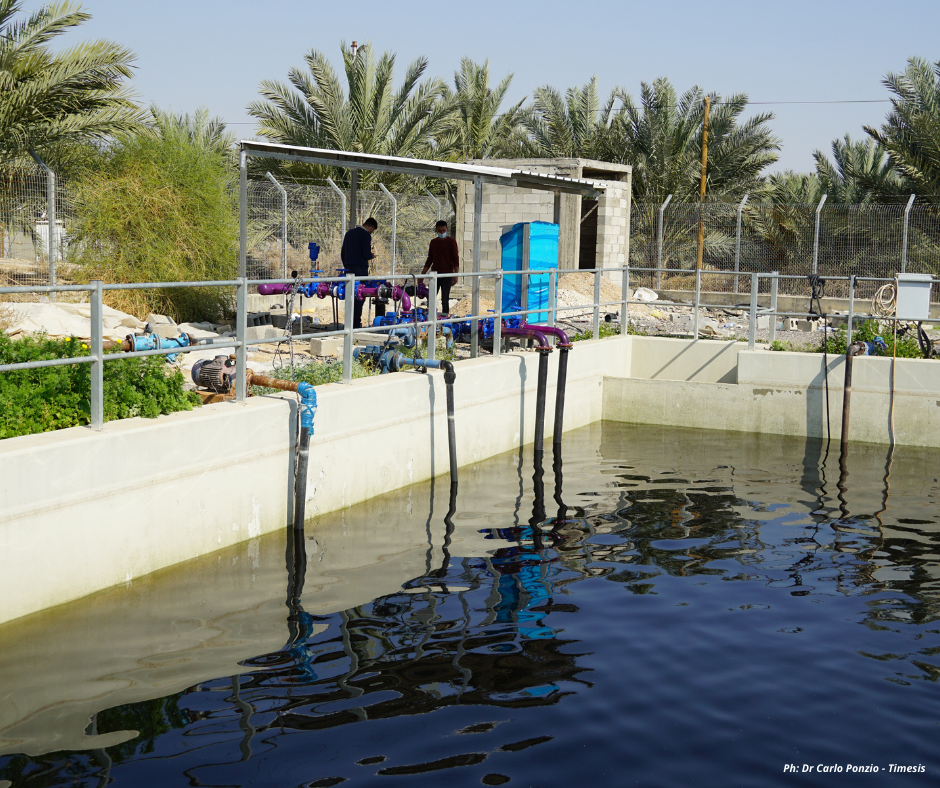

The treated wastewater is blended with wadi kelt brackish water, which has water only in winter.
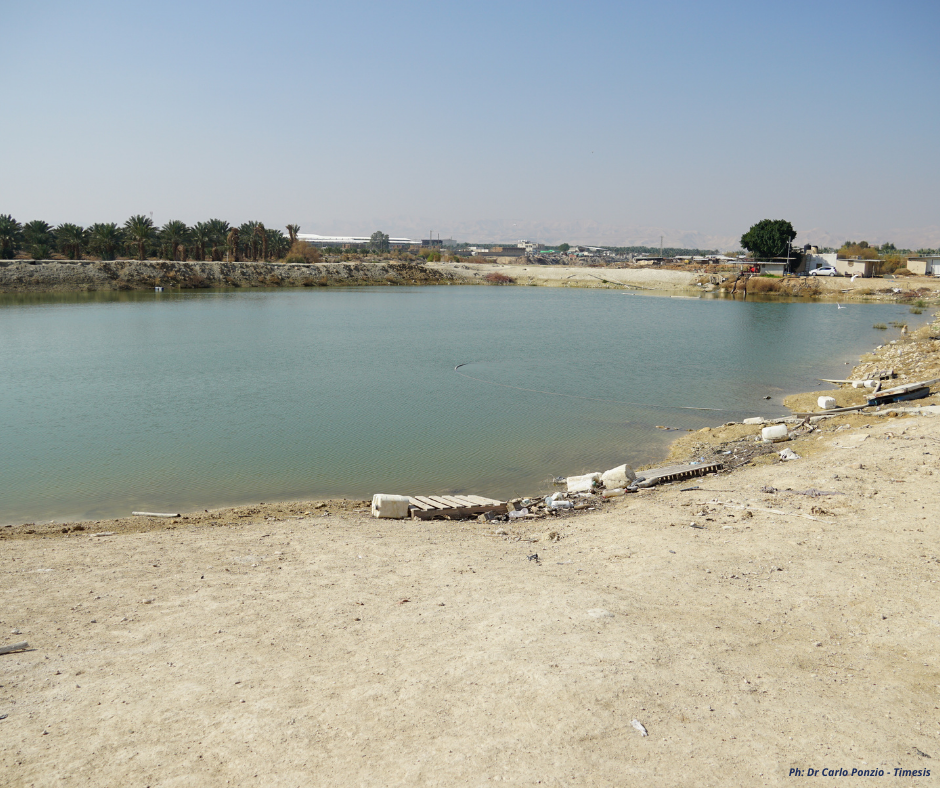


The mixing activity takes place in a water basin of 80 thousand m3, this will be then blended with saline water in a blending ratio which will improve water quality In addition, the use of the wadi water will alleviate the pressure on the ground water used by the armers in irrigation.
The project is currently completing the connections to the electricity network to activate the pumping stations to allow the 3 types of water to be blended and used in irrigation. The proportions of the respective 3 types of water are being studied, in order to obtain high-quality irrigation water.