Tunisie: le projet MEDISS explore l'utilisation de l'argile comme matériau naturel pour le traitement des eaux usées

Ce contenu est disponible uniquement en anglais
MEDISS tunisian project partner, Institut des Régions Arides (IRA Médenine), carried out in April a site visit to Mount Aidoudi to sample a clay deposit located in the north of the El Hamma region (Tunisia).
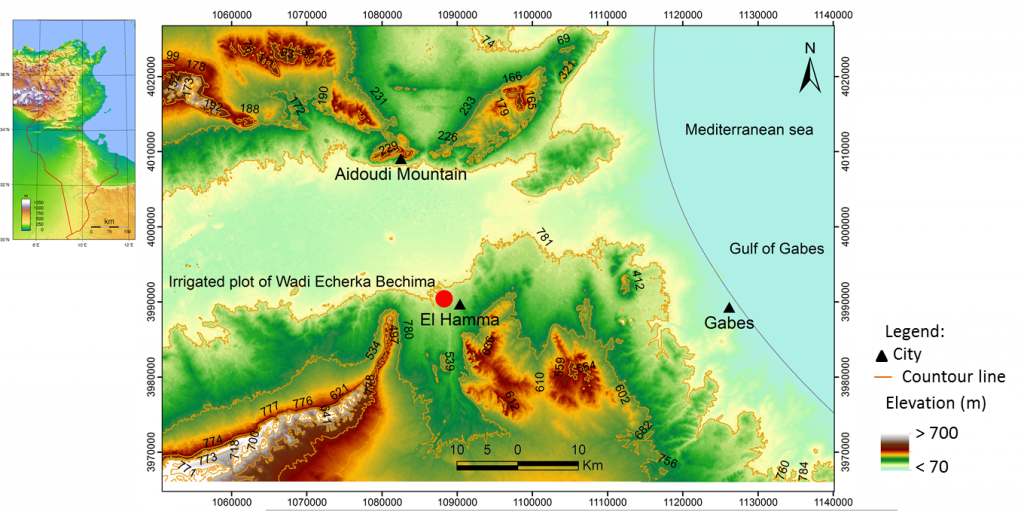
The sampling site is about 15 km away from the irrigated plot of Wadi Echerka Bechima, the MEDISS pilot site in Tunisia. The proximity between the clay deposit and the pilot site will make it easier for farmers to extract the clay to be used as filtration mixture for the wastewater treatment system.
The main objective of the visit was to investigate and understand the properties of clay as filter material in the wastewater treatment system used for irrigation, which will be realized in the framework of the MEDISS project.
In particular, IRA Médenine researchers studied the behavior of local material, montmorillonite clay, and the valorization of this natural resource in the field of wastewater treatment.
Montmorillonite (MMT) is the most commonly used clay mineral, and it demonstrates good biocompatibility and biodegradability in combination with good mechanical properties.
Sampled clays from IRA Médenine will be analyzed and tested in laboratory filtration trials before being used in the wastewater treatment system in Wadi Echerka Bechima.